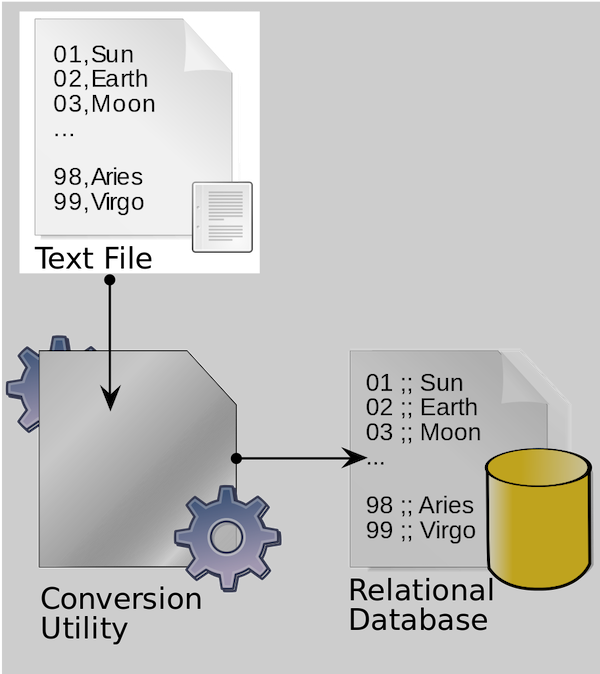
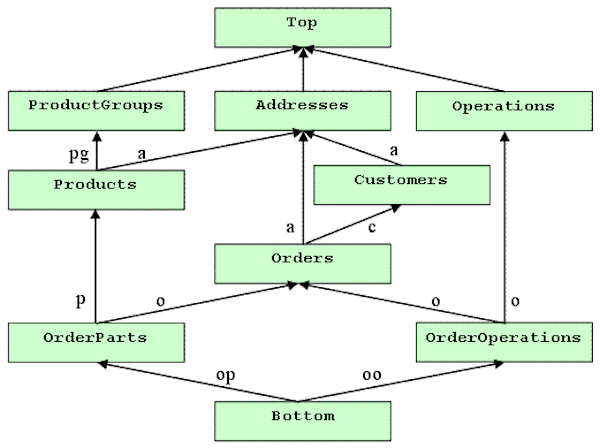
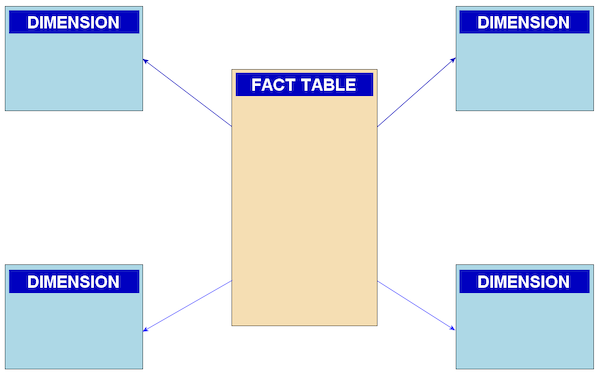
Data model (or Datamodel) is an abstract model that organizes elements of data and standardizes how they relate to one another and to the properties of real-world entities. For instance, a data model may specify that the data element representing a car be composed of a number of other elements which, in turn, represent the color and size of the car and define its owner.
The main aim of data models is to support the development of information systems by providing the definition and format of data.
Three perspectives
- Conceptual data model : describes the semantics of a domain, being the scope of the model. This consists of entity classes, representing kinds of things of significance in the domain, and relationship assertions about associations between pairs of entity classes. A conceptual schema specifies the kinds of facts or propositions that can be expressed using the model.
- Logical data model : describes the semantics, as represented by a particular data manipulation technology. This consists of descriptions of tables and columns, object oriented classes, and XML tags, among other things.
- Physical data model : describes the physical means by which data are stored. This is concerned with partitions, CPUs, tablespaces, and the like.
Database model
Object-relational Model Object-role Modeling
Data model theory
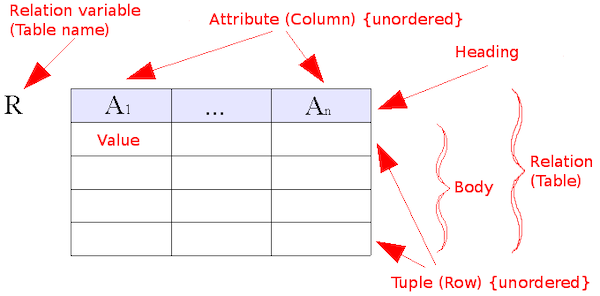
- The structural part: a collection of data structures which are used to create databases representing the entities or objects modeled by the database.
- The integrity part: a collection of rules governing the constraints placed on these data structures to ensure structural integrity.
- The manipulation part: a collection of operators which can be applied to the data structures, to update and query the data contained in the database.
Data Vault Modeling
The data vault methodology is not a new idea; Dan Linstedt, the creator of the method, started developing it in the 1990’s. As defined by Linstedt in an article published to the Data Administration Newsletter in 2002:
The Data Vault is a detail oriented, historical tracking and uniquely linked set of normalized tables that support one or more functional areas of business. It is a hybrid approach encompassing the best of breed between 3rd normal form (3NF) and star schema. The design is flexible, scalable, consistent and adaptable to the needs of the enterprise. It is a data model that is architected specifically to meet the needs of enterprise data warehouses.
The data vault model contains three main entities; hubs, links, and satellites. There is a single hub table for each business key, and it includes some metadata about these keys as well. In some cases, a business entity cannot be identified by a single key, so composite keys are allowed. Link tables connect two or more hubs - they define the relationships and interactions between entities. Satellite tables contain non-identifying descriptive attributes about hubs and links.