Internet is the global system of interconnected computer networks that uses the Internet protocol suite (TCP/IP) to communicate between networks and devices.
- Internet Protocol
- Internet protocol suite
- World Wide Web
- List of network protocols (OSI model)
- List of TCP and UDP port numbers
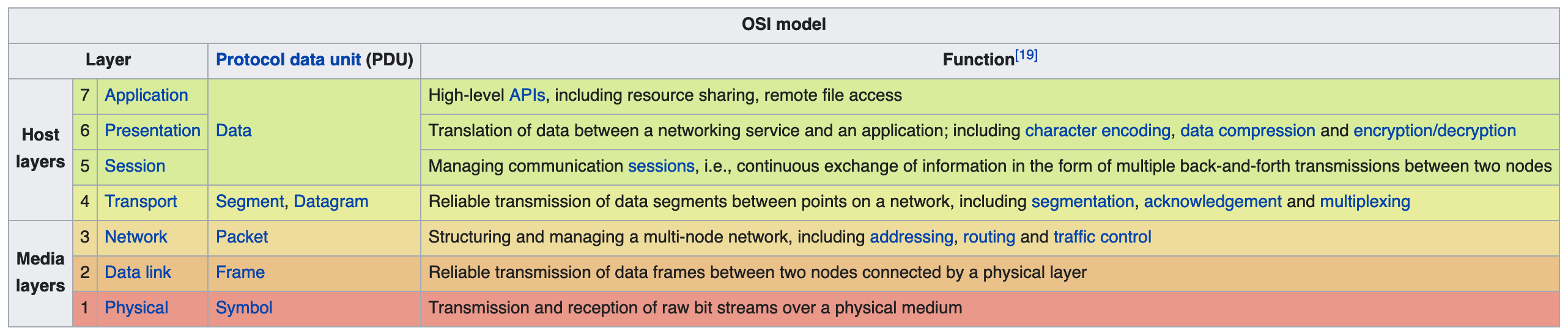
The Open Systems Interconnection model (OSI model) is a conceptual model that characterises and standardises the communication functions of a telecommunication or computing system without regard to its underlying internal structure and technology. Its goal is the interoperability of diverse communication systems with standard communication protocols. The model partitions a communication system into abstraction layers.
Request for Comments (RFC), in information and communications technology, is a type of text document from the technology community. An RFC document may come from many bodies including from the Internet Engineering Task Force (IETF), the Internet Research Task Force (IRTF), the Internet Architecture Board (IAB), or from independent authors. The RFC system is supported by the Internet Society (ISOC).
Internet Protocol
The Internet Protocol (IP) is the principal communications protocol in the Internet protocol suite for relaying datagrams across network boundaries. Its routing function enables internetworking, and essentially establishes the Internet.
The Internet Corporation for Assigned Names and Numbers (ICANN) is an American multi-stakeholder group and nonprofit organization responsible for coordinating the maintenance and procedures of several databases related to the namespaces and numerical spaces of the Internet, ensuring the network’s stable and secure operation.
Internet protocol suite
The Internet protocol suite is the conceptual model and set of communications protocols used in the Internet and similar computer networks. It is commonly known as TCP/IP because the foundational protocols in the suite are the Transmission Control Protocol (TCP) and the Internet Protocol (IP). During its development, versions of it were known as the Department of Defense (DoD) model because the development of the networking method was funded by the United States Department of Defense through DARPA. Its implementation is a protocol stack.
World Wide Web
The World Wide Web (WWW), commonly known as the Web, is an information system where documents and other web resources are identified by Uniform Resource Locators (URLs, such as https://example.com/){:target=”_blank”}, which may be interlinked by hypertext, and are accessible over the Internet. The resources of the Web are transferred via the Hypertext Transfer Protocol (HTTP) and may be accessed by users by a software application called a web browser and are published by a software application called a web server.
List of network protocols (OSI model)
List of TCP and UDP port numbers
TCP and UDP is located at layer 4 (Transport Layer)